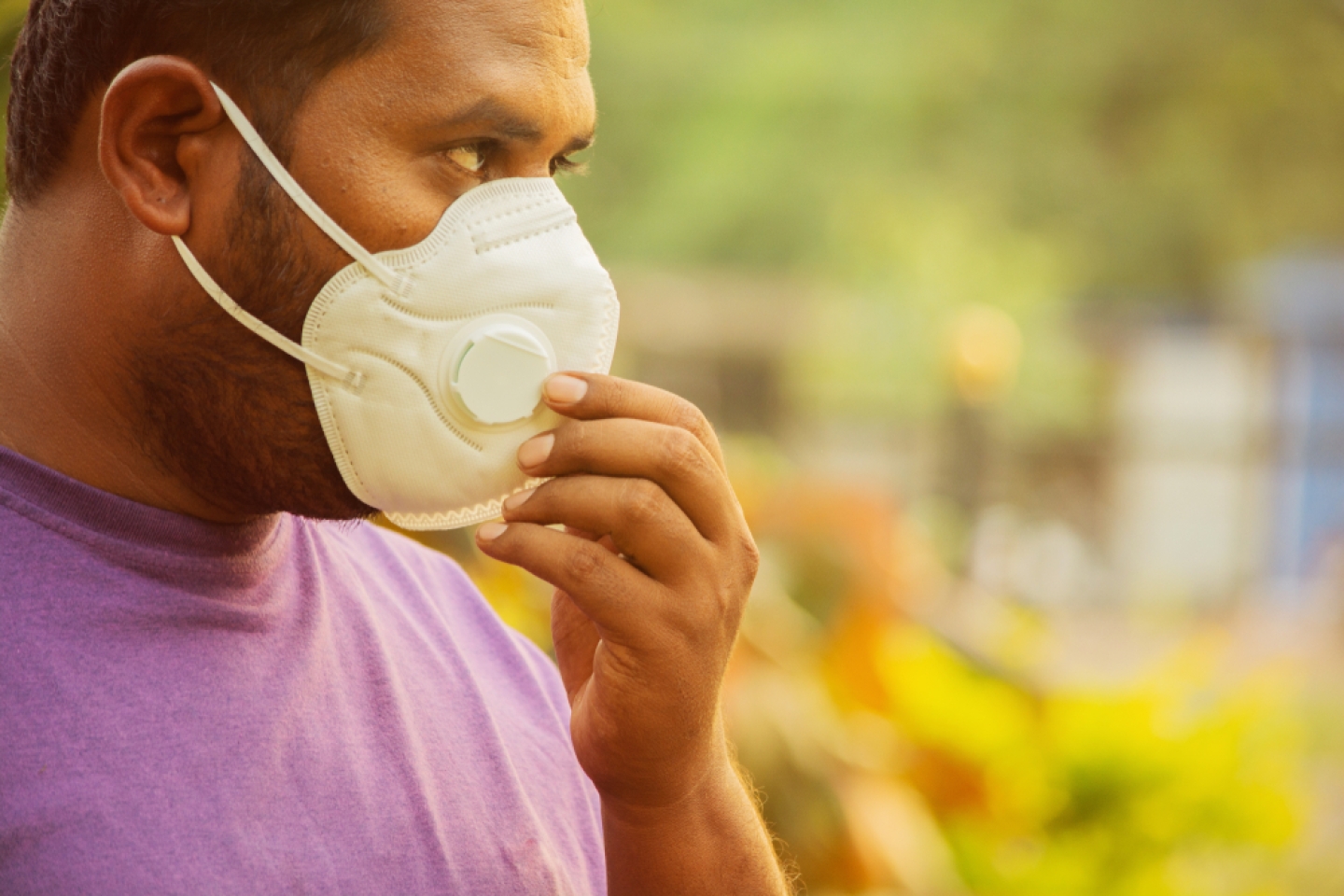
Maintaining good air quality in the workplace is essential, especially in environments where hazardous airborne particles, gases, or vapors are present. Poor air quality can pose significant health risks, leading to respiratory diseases, lung damage, and other long-term health effects. Fortunately, using the right respiratory protection can help safeguard workers’ health and ensure a safer work environment.
In this article, we’ll explore the importance of air quality in the workplace, how to assess potential hazards, and how to choose the right respiratory protection to keep employees safe.
1. Why Air Quality Matters in the Workplace
Air quality is a critical factor in maintaining a healthy and safe work environment. Poor air quality can result from dust, chemical fumes, toxic gases, or biological contaminants that workers inhale over time. When workers are exposed to these airborne hazards, it can lead to serious health problems, including:
- Respiratory infections
- Lung diseases such as asthma or chronic bronchitis
- Long-term conditions like silicosis or asbestosis
- In extreme cases, exposure to toxic substances may even be fatal
Understanding the air quality in your workplace is the first step toward implementing appropriate safety measures.
2. Assessing Air Quality Hazards
Before selecting any respiratory protection, it’s essential to assess the specific air quality hazards present in your work environment. Hazardous particles may come in various forms, such as dust, mists, vapors, or fumes. It’s important to conduct an air quality evaluation to determine the levels and types of contaminants your workers may be exposed to.
In some cases, air quality may not be consistently poor, but periodic monitoring can reveal when certain tasks generate higher levels of airborne hazards. For example, activities like welding, grinding, or working with chemicals can introduce more particles into the air. Once you’ve assessed the air quality, you can implement control measures such as ventilation, and where those are insufficient, ensure proper respiratory protection.
3. Choosing the Right Respiratory Protection
Selecting the appropriate respiratory protection is key to safeguarding workers from harmful airborne substances. Respiratory protection can range from simple disposable masks to more advanced full-face respirators. The type of protection required will depend on the specific hazards present in your environment.
Here are the main types of respiratory protection:
- Disposable Respirators: Suitable for low-level dust and particles but offer minimal protection against gases and vapors.
- Half-Mask Respirators: Provide protection for the nose and mouth and can be equipped with filters or cartridges to block out specific contaminants.
- Full-Face Respirators: Cover the entire face, offering protection for the respiratory system and the eyes, making them ideal for environments with both airborne particulates and chemical splashes.
- Powered Air-Purifying Respirators (PAPRs): These use a fan to draw air through filters and offer a higher level of protection, suitable for more dangerous environments.
It’s also essential to match the respirator with the correct filter or cartridges designed to protect against specific contaminants, whether they are dust, gases, or vapors.
4. Respirator Fit and Maintenance
Choosing the right respirator is only half the battle. For it to function effectively, it must fit properly. Poorly fitting respirators can allow harmful contaminants to bypass the filters, putting workers at risk. Conducting regular fit tests ensures that the respirator forms a proper seal with the face, blocking out harmful substances.
Fit testing is particularly important for tight-fitting respirators like full-face or half-mask respirators. Regular maintenance and care, such as replacing filters and cleaning the respirator, are also critical for ensuring continued protection. For more information on how to care for your respirator, check out our guide on respirator maintenance.
5. Ventilation and Engineering Controls
While respirators provide direct protection, they are not the only way to improve air quality in the workplace. Engineering controls, such as proper ventilation systems, can help reduce the concentration of airborne contaminants, making the air safer to breathe.
Ventilation systems, such as local exhaust ventilation (LEV), capture harmful particles at their source and remove them from the work area. In some cases, ventilation may be sufficient to reduce airborne hazards to a safe level, but where that is not possible, respiratory protection will still be necessary.
6. Training and Education on Respiratory Safety
To ensure workers are using their respiratory protection effectively, it’s crucial to provide adequate training and education. Workers should be trained on:
- How to properly wear and adjust their respirator
- The importance of maintaining and inspecting their equipment
- Understanding the limitations of their respirator and when to replace filters or cartridges
- Recognizing the signs of poor air quality and when to use additional protective measures
Well-trained workers are more likely to use their equipment correctly, reducing the risk of respiratory illnesses or accidents.
Conclusion
Maintaining good air quality in the workplace and providing appropriate respiratory protection are essential for safeguarding the health of workers. By understanding the specific air quality hazards present, selecting the right respiratory protection, and ensuring proper fit and maintenance, you can help protect your employees from the risks of poor air quality. Additionally, integrating engineering controls like ventilation and offering comprehensive training can further enhance safety.